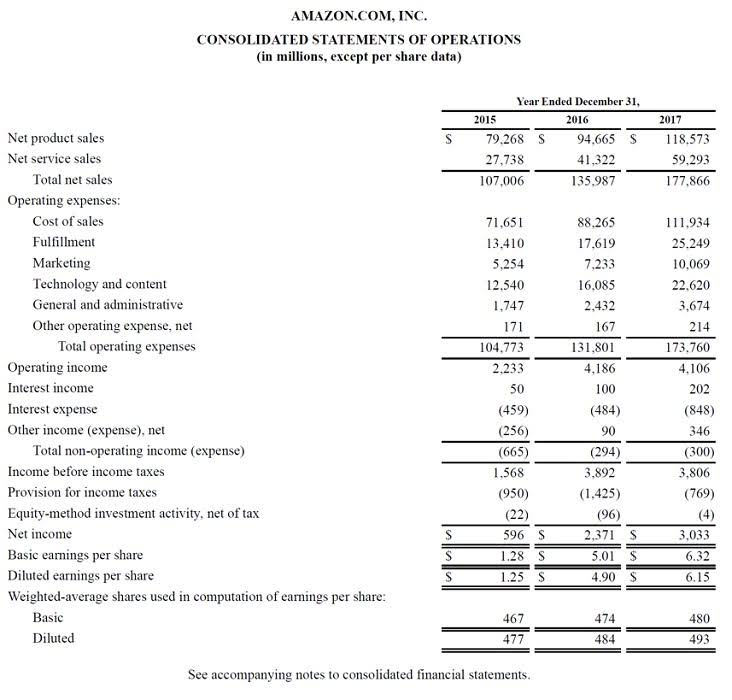
To calculate this, we first need to identify the total direct cost of production and the total overhead cost for the specific period. Thus, this total overhead is divided by the total direct cost to ascertain the single plantwide overhead rate. The advent of sophisticated software and technological tools has transformed the approach to calculating overhead rates. These systems can track and allocate costs with greater accuracy by using real-time data from various departments within a company. For instance, an ERP system can automatically assign overhead costs to products as they move through the production process, based on the actual resources consumed.
How to Determine Product Costs Using the Plantwide Allocation Approach
It involves a series of calculations and decisions that, while seemingly straightforward, can significantly influence the financial outcomes of a business. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of historical and operational data to identify trends and predict future overhead costs. By understanding these patterns, companies can proactively manage their overhead, for example, by scheduling production runs during off-peak energy hours to reduce utility costs. Predictive analytics can also help in determining the impact of overhead costs on product pricing and profitability, enabling more informed strategic decisions. Notice that under this allocation method, using direct machine hours instead of units, we have a dramatically different outcome.
- Thus, this total overhead is divided by the total direct cost to ascertain the single plantwide overhead rate.
- The same manufacturing plant also produces 1000 units of another product, which we call product Y, using 500 labor hours.
- The Plantwide overhead rate is the overhead rate that companies use to allocate their entire manufacturing overhead costs to their line of products and other cost objects.
- This base is a measure of activity, such as direct labor hours or machine hours, that is used to assign overhead costs to products.
- These estimates are based on the previous year’s overhead costs and direct labor hours and are adjusted for expected increases in demand the coming year.
- Create a Full Dynamic Financial Model in 2 Days (6 hours) | Any Graduate Or Professional is eligible | Build & Forecast IS, BS, CF from Scratch.
The application and impact of overhead rates exhibit considerable variation across different industries due to the unique nature of their production processes and cost structures. In manufacturing, where the production process is equipment-intensive, overhead rates are often driven by machine-related expenses. Conversely, in service industries like consulting or software development, overhead rates are more likely to be influenced by employee-related costs, such as salaries and benefits. Explore the significance of plantwide overhead rate in product costing and how it streamlines financial processes across various industries. One cost pool accounts for all overhead costs, and therefore one predetermined overhead rate is used to apply overhead costs to products. The significance of the plantwide overhead rate extends beyond mere accounting; it influences strategic decision-making and can impact a company’s financial health.
As a result, some products might be overcosted while others are undercosted, leading to potential pricing and profitability issues. Despite its limitations, a plantwide overhead rate can still be useful when overhead costs are relatively uniform across all products and departments. This base is a measure of activity, such as direct labor hours or machine hours, that is used to assign overhead costs to products. The choice of allocation base should reflect the way in which resources are consumed in the production process. For example, if a company predominantly incurs overhead costs related to machinery, machine hours might be the most representative allocation base. The selection of the allocation base is a critical decision as it directly affects the accuracy of the overhead costs allocated to each product.
Once we have determined our allocation rate, we apply that rate to each product or product line in order to assign costs to individual items or batches. As we move on to more complex costing systems, remember that these systems are more expensive to implement. Thus the benefits of having improved cost information must outweigh the costs of obtaining the information. Create a Full Dynamic Financial Model in 2 Days (6 hours) | Any Graduate Or Professional is eligible | Build & Forecast IS, BS, CF from Scratch.
Overhead rates in construction can include the costs of site security, equipment rental, and project management, which vary widely from project to project. This necessitates a more granular approach to overhead allocation to ensure that each project bears its fair share of the indirect costs. Both plantwide rate and departmental rate are means of estimating the overhead cost allocation to products and services. However, there are a few points of differences that make each preferable by firms as per their requirements and suitability. As the name implies, these overhead rates take into account the entire plant and not a particular segment or department.
It is essential to ensure that all relevant overhead costs are included to avoid under- or overestimating the rate, which could lead to pricing and profitability issues. By allocating fixed manufacturing overhead by machine hours, the deluxe purse is actually costing more to produce than it is selling for. Annual overhead costs are estimated and direct labor hours are used for the plantwide allocation base. Understanding the true cost of manufacturing a product is crucial for businesses to price their goods competitively while ensuring profitability. One key component in this process is the plantwide overhead rate, which allocates indirect costs to products.
Quiz 4: Activity-Based Costing and Analysis
The calculation of a product’s cost involves three components—direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead. Organizations that use a plantwide allocation approach typically have simple operations with a few similar products. This information, combined with the overhead cost per unit, gives us what we need to determine the product cost per unit for each model. Management may not want more accurate product cost information or may the cost object of the plantwide overhead rate method is not have the resources to implement a more complex accounting system.
What is the Plantwide Allocation of Costs?
As industries evolve and technology advances, the methods for calculating and applying these rates are also changing, prompting a reevaluation of traditional costing practices. We’ll study how this works in the next section, but first check your understanding of using a single rate to allocate fixed manufacturing overhead to products. Implementing departmental rates requires a detailed understanding of the activities and costs within each department.
- Both plantwide rate and departmental rate are means of estimating the overhead cost allocation to products and services.
- To calculate this, we first need to identify the total direct cost of production and the total overhead cost for the specific period.
- The significance of the plantwide overhead rate extends beyond mere accounting; it influences strategic decision-making and can impact a company’s financial health.
- By assigning a unique overhead rate to each department, businesses can achieve a more accurate allocation of indirect costs, leading to more precise product costing.
Technology in Overhead Calculation
If our standard direct labor cost is the same for both purses, these two calculations will produce the same results, so in this lesson, we’ll use DL$. However, if workers producing deluxe purses are more highly paid than workers producing basic purses, the outcome between the two direct labor methods would be different. One more approach is to calculate the plantwide overhead rate using an alternative approach or direct cost method.
By calculating separate overhead rates for each department, a company can assign costs based on the actual resources each product consumes as it moves through the production process. This method is particularly beneficial for companies with diverse product lines or complex manufacturing processes, where a plantwide rate might obscure the true cost of production. These costs are not directly tied to the production of any single product but are necessary for the operation of the business as a whole. For instance, if a company incurs $500,000 in total overhead costs in a year, this figure serves as the starting point for calculating the plantwide overhead rate.
Products are the first stage cost objects when using a departmental overhead rate method.
The same manufacturing plant also produces 1000 units of another product, which we call product Y, using 500 labor hours. Manufacturing overhead cost per unit is Base Rate × A direct labor hours + Base Rate × B direct labor hours. The process of determining the plantwide overhead rate is a foundational step in product costing that affects the accuracy of cost information.
Allocating Based on Direct Machine Hours
The plantwide overhead rate is a single overhead rate that a company uses to allocate all of its manufacturing overhead costs to products or cost objects. It is typically based on one cost driver, such as direct labor hours or machine hours, for the entire plant. This method is easy to apply and provides a straightforward way to assign overhead costs in smaller or less complex manufacturing environments. However, it may oversimplify the true consumption of overhead resources if different products or departments use overhead at varying rates.
By leveraging these technologies, businesses can move beyond static overhead rates, adjusting them in response to changes in production activity or cost structures. It means the total number of direct labor hours is taken as the denominator, which is divided by the numerator as the total overhead cost of the company. These estimates are based on the previous year’s overhead costs and direct labor hours and are adjusted for expected increases in demand the coming year. The manufacturing plant requires 1000 labor hours to manufacture 500 units of a specific product, which we assume as product X.